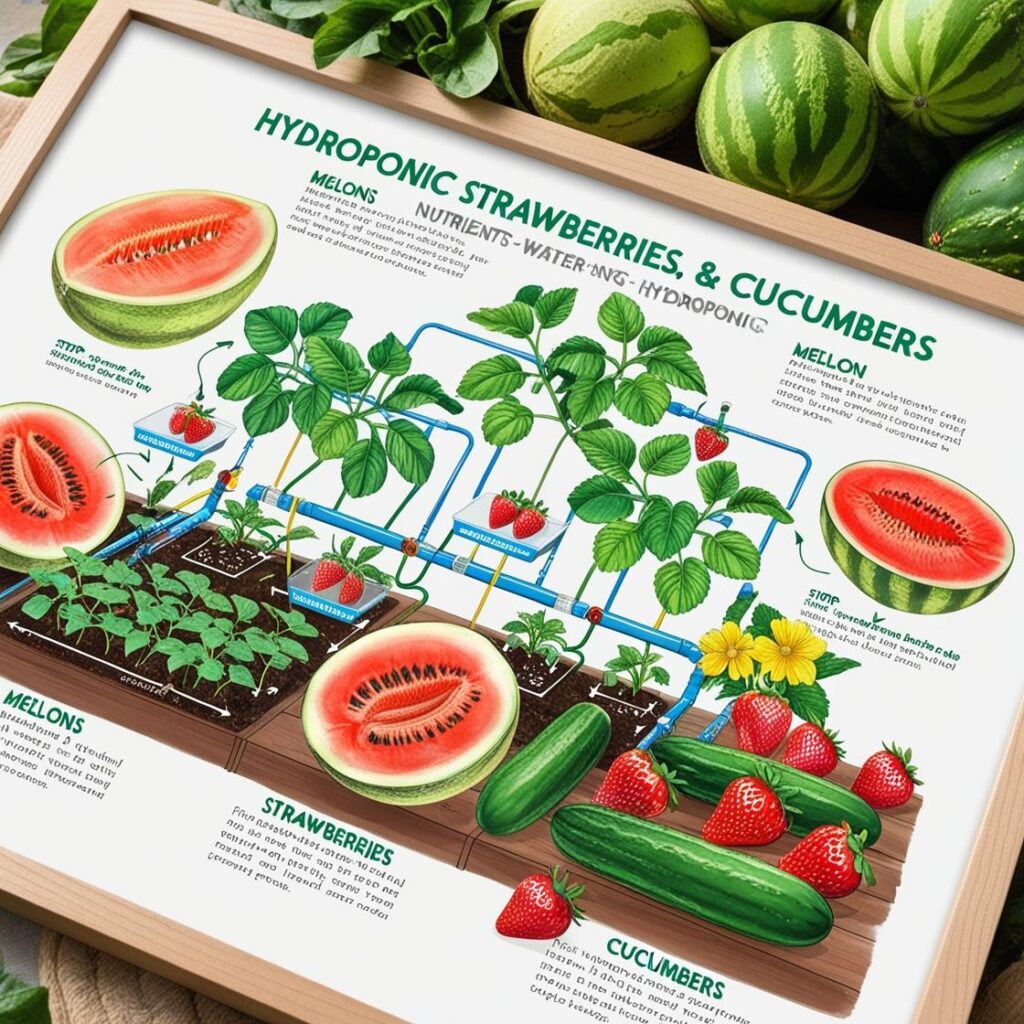
Imagine biting into a juicy, sweet melon, freshly picked from your garden. Now picture achieving this without the usual soil-related hassles. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just getting started, this guide will walk you through the art of hydroponics for melons, strawberries, and cucumbers. With a touch of science and a bit of care, you can enjoy bountiful harvests of these delicious fruits. Let’s dive in!

Cultivating Melons: A Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction to Melons
Originating from the subtropical regions of Asia, melons have been cherished for centuries. Belonging to the same botanical family as cucumbers, they come in various types, including sugar melons, cantaloupe melons, and nettle melons.
Types of Melons
- Cantaloupe Melons: Recognizable by their firm orange flesh and hard, scaly rind with grooves.
- Honeydew Melons: These have smooth or ribbed yellow to greenish skins, with flesh that can be yellowish, white, or orange.
- Net Melons: Known for their net-patterned shells and flesh that ranges from green to salmon-colored.
Growing Conditions
Melons thrive in warm temperatures, between 20 to 30 degrees Celsius. Here’s how to get started:
- Sowing Seeds: In April, plant seeds 1-2 cm deep in small pots and place them on a sunny windowsill.
- Transplanting: Move the seedlings outdoors in mid-May or early June, ensuring they’re spaced 80 cm apart.
Care Tips
- Heat and Sunlight: Melons need plenty of heat and sunlight to develop their sweetness and aroma.
- Soil Preparation: Use compost and slow-release fertilizer in the planting hole.
- Pruning: To maximize fruit production, prune the main shoot after the fourth or fifth leaf and repeat this for the side shoots.
Hydroponics for Strawberries: Boosting Yield and Quality
Why Hydroponics?
Hydroponic systems provide strawberries with optimal nutritional conditions, enhancing their size, sweetness, and overall quality. This method also minimizes soil-related issues like fungi and mold.
Hydroponic Setup for Strawberries
- Growing Medium: Use plastic bags filled with a mix of white peat and pearlite, ensuring a light and airy environment.
- Nutrient Solutions: Maintain a consistent supply of nutrients and water.
- Protection: Utilize plastic tunnels for thermal insulation and to extend the growing season.
Benefits
- Higher Quality: Hydroponically grown strawberries are cleaner and more uniform in size.
- Longer Shelf Life: These strawberries are less fibrous and have a higher sugar content, making them more durable for transport.
Mastering Cucumber Hydroponics: Tips and Tricks
Choosing Varieties
Opt for popular hydroponic varieties like “European” or “long English” cucumbers, as well as Beit Alpha, Japanese, or Persian varieties.
Setting Up Your Hydroponic System
- Materials Needed:
- Expanded clay
- Plastic pipes
- Pump
- Mineral wool
- Compost layer
- Medium gravel
- Water
Growing Process
- Seed Sowing: Soak cork stoppers in a nutrient solution and place cucumber seeds in the center.
- Transplanting: Move seedlings to cubes treated with nutrient solutions.
- Final Planting: Transfer mature seedlings to mats, maintaining a warm temperature of +22-25°C.
Care Instructions
- Pruning: Remove the main stalk before fruiting to encourage healthy growth.
- Watering: Ensure cucumbers are watered properly, with spraying done early in the morning and late in the afternoon.
- Temperature and Humidity: Maintain a temperature of +19-22°C and humidity levels between 70-80% to prevent diseases.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Fast growth
- Reduced use of harmful chemicals
- Space efficiency
- No need for soil
Disadvantages:
- Initial setup costs
- Regular monitoring of temperature and nutrients

Summary for Instagram Reels and Infographics
Quick Tips for Growing Melons, Strawberries, and Cucumbers Hydroponically:
- Melons: Warm temperatures, compost-enriched soil, prune main and side shoots.
- Strawberries: Use plastic bags with peat, consistent nutrients, protect with plastic tunnels.
- Cucumbers: Choose suitable varieties, use expanded clay and mineral wool, maintain proper watering and temperature.
By following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying fresh, hydroponically grown fruits from your garden! Happy gardening!
Discover the Secrets of Growing Melons, Strawberries, and Cucumbers Hydroponically
Imagine biting into a juicy, sweet melon, freshly picked from your garden. Now picture achieving this without the usual soil-related hassles. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just getting started, this guide will walk you through the art of hydroponics for melons, strawberries, and cucumbers. With a touch of science and a bit of care, you can enjoy bountiful harvests of these delicious fruits. Let’s dive in!
Cultivating Melons: A Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction to Melons
Originating from the subtropical regions of Asia, melons have been cherished for centuries. Belonging to the same botanical family as cucumbers, they come in various types, including sugar melons, cantaloupe melons, and nettle melons.
Types of Melons
- Cantaloupe Melons: Recognizable by their firm orange flesh and hard, scaly rind with grooves.
- Honeydew Melons: These have smooth or ribbed yellow to greenish skins, with flesh that can be yellowish, white, or orange.
- Net Melons: Known for their net-patterned shells and flesh that ranges from green to salmon-colored.
Growing Conditions
Melons thrive in warm temperatures, between 20 to 30 degrees Celsius. Here’s how to get started:
- Sowing Seeds: In April, plant seeds 1-2 cm deep in small pots and place them on a sunny windowsill.
- Transplanting: Move the seedlings outdoors in mid-May or early June, ensuring they’re spaced 80 cm apart.
Care Tips
- Heat and Sunlight: Melons need plenty of heat and sunlight to develop their sweetness and aroma.
- Soil Preparation: Use compost and slow-release fertilizer in the planting hole.
- Pruning: To maximize fruit production, prune the main shoot after the fourth or fifth leaf and repeat this for the side shoots.
Hydroponics for Strawberries: Boosting Yield and Quality
Why Hydroponics?
Hydroponic systems provide strawberries with optimal nutritional conditions, enhancing their size, sweetness, and overall quality. This method also minimizes soil-related issues like fungi and mold.
Hydroponic Setup for Strawberries
- Growing Medium: Use plastic bags filled with a mix of white peat and pearlite, ensuring a light and airy environment.
- Nutrient Solutions: Maintain a consistent supply of nutrients and water.
- Protection: Utilize plastic tunnels for thermal insulation and to extend the growing season.
Benefits
- Higher Quality: Hydroponically grown strawberries are cleaner and more uniform in size.
- Longer Shelf Life: These strawberries are less fibrous and have a higher sugar content, making them more durable for transport.
Mastering Cucumber Hydroponics: Tips and Tricks
Choosing Varieties
Opt for popular hydroponic varieties like “European” or “long English” cucumbers, as well as Beit Alpha, Japanese, or Persian varieties.
Setting Up Your Hydroponic System
- Materials Needed:
- Expanded clay
- Plastic pipes
- Pump
- Mineral wool
- Compost layer
- Medium gravel
- Water
Growing Process
- Seed Sowing: Soak cork stoppers in a nutrient solution and place cucumber seeds in the center.
- Transplanting: Move seedlings to cubes treated with nutrient solutions.
- Final Planting: Transfer mature seedlings to mats, maintaining a warm temperature of +22-25°C.
Care Instructions
- Pruning: Remove the main stalk before fruiting to encourage healthy growth.
- Watering: Ensure cucumbers are watered properly, with spraying done early in the morning and late in the afternoon.
- Temperature and Humidity: Maintain a temperature of +19-22°C and humidity levels between 70-80% to prevent diseases.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Fast growth
- Reduced use of harmful chemicals
- Space efficiency
- No need for soil
Disadvantages:
- Initial setup costs
- Regular monitoring of temperature and nutrients
Summary for Instagram Reels and Infographics
Quick Tips for Growing Melons, Strawberries, and Cucumbers Hydroponically:
- Melons: Warm temperatures, compost-enriched soil, prune main and side shoots.
- Strawberries: Use plastic bags with peat, consistent nutrients, protect with plastic tunnels.
- Cucumbers: Choose suitable varieties, use expanded clay and mineral wool, maintain proper watering and temperature.
By following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying fresh, hydroponically grown fruits from your garden! Happy gardening!
Unveiling the Secrets of Watercress, Fennel, and Borage: Your Guide to Growing and Using These Nutrient-Packed Plants
Growing your own herbs and vegetables can be both rewarding and beneficial for your health. Today, let’s explore how to cultivate and utilize watercress, fennel, and borage. These plants are not only easy to grow but also packed with nutrients and medicinal properties. Perfect for both beginners and seasoned gardeners, this guide will take you through the essentials of growing these plants and reaping their benefits.
Watercress: The Nutrient Powerhouse
Introduction to Watercress
Watercress, scientifically known as Nasturtium officinale, is a highly nutritious plant historically valued for its medicinal properties. Its name, derived from the Latin “nasus tortus” (twisted nose), hints at the plant’s slightly pungent taste.
Nutritional and Medicinal Benefits
Watercress is a rich source of vitamins C, A, K, and B2, making it a fantastic addition to your diet. It also contains iodine, iron, calcium, and mustard oils, which contribute to its antibacterial and digestive benefits. Traditionally, watercress has been used to treat scurvy, purify the blood, and support respiratory and kidney health.
Cultivation Tips
- Growing Conditions: Watercress thrives in shallow, clean water with a slight current, such as the edges of streams.
- Starting Seeds: Press seeds lightly onto moist soil and keep them at a temperature of 20°C. They should germinate in about a week.
- Planting: Once seedlings reach 8-10 cm, transfer them to a suitable water source or hydroponic setup.
Care and Harvesting
- Location: Choose a shady spot with clear, shallow water.
- Water Depth: Maintain water levels between 5 to 20 cm.
- Harvesting: Regularly harvest leaves to encourage new growth and ensure a continuous supply.
Fennel: The Mediterranean Marvel
Introduction to Fennel
Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare), native to the Mediterranean, is celebrated for its sweet, aniseed flavor. This versatile plant can be used in various culinary and medicinal applications.
Uses in the Kitchen
- Leaves and Tubers: Ideal for adding a fresh flavor to salads and fish dishes.
- Seeds: Perfect for spicing soups, sauces, meats, and even baked goods and alcoholic beverages.
Medicinal Benefits
Fennel is renowned for its ability to relieve flatulence, abdominal pain, and respiratory issues. It also helps soothe eye inflammation when used as an infusion.
Cultivation Tips
- Climate: Fennel prefers warm, sunny locations.
- Soil: Plant in light, well-draining soil.
- Sensitivity: Be mindful of fennel’s sensitivity to overly moist conditions.
Care and Harvesting
- Watering: Ensure the soil is not too moist to avoid root rot.
- Harvesting: Regularly trim leaves and tubers to promote healthy growth and prevent the plant from becoming leggy.
Borage: The Cucumber-Tasting Herb
Introduction to Borage
Borage (Borago officinalis), often referred to as the cucumber herb, brings a fresh, cucumber-like flavor to dishes. It’s not just a culinary delight but also has medicinal uses.
Culinary Uses
Borage leaves are excellent in salads and as a garnish for various spreads. Its flowers can also add a pop of color and flavor to your dishes.
Medicinal Benefits
The seeds and oil from borage are commonly used to treat skin complaints, making it a valuable addition to your herbal medicine cabinet.
Cultivation Tips
- Growing Conditions: Borage is relatively easy to grow and does well in most garden soils.
- Starting Seeds: Plant seeds directly into the ground, lightly covering them with soil.
Care and Harvesting
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Harvesting: Regularly pick leaves and flowers to encourage new growth.
Summary for Instagram Reels and Infographics
Quick Tips for Growing and Using Watercress, Fennel, and Borage:
- Watercress: Start seeds in moist soil, transfer to shallow water sources, and enjoy nutrient-packed leaves.
- Fennel: Plant in sunny, well-draining soil, use leaves and seeds in cooking, and harvest regularly for health benefits.
- Borage: Easy to grow, adds a cucumber flavor to dishes, and has medicinal properties for skin health.
By following these guidelines, you’ll be well on your way to cultivating a garden filled with these versatile and nutritious plants. Enjoy the process and the delicious, healthy rewards!
Valerian: The Soothing Herb
Introduction to Valerian
Valerian (Valeriana officinalis) is an herbaceous plant native to central Europe and Asia, now widespread in western Europe and North America. It can grow up to 1.5 meters tall and is known for its distinctive rhizome, which emits an unpleasant odor.
Habitat and Cultivation
Valerian thrives in humid environments such as riverbanks and wooded areas but can also be cultivated in gardens. It prefers temperate climates and can withstand temperatures as low as -15°C. Valerian can be propagated by seeds, rhizome division, or tuft division.
- Soil Preparation: Work the soil deeply before sowing.
- Seed Multiplication: Best done in spring using seedbeds, though growth is slow.
Uses
Valerian is primarily known for its sedative properties, often used to treat insomnia and anxiety.
Hydroponic Nutrient Solutions
Introduction
In hydroponics, the nutrient solution is critical as it provides all the necessary nutrients for plant growth. Understanding the composition, pH, and electrical conductivity (EC) of the solution is essential for successful cultivation.
Standard Nutrient Solutions
Several standard nutrient solutions are commonly used, including the Hoagland solution, Steiner solution, and Bollard solution. These are good starting points but may need adjustments based on specific growing conditions and water quality.
Electrical Conductivity (EC)
EC measures the total dissolved salts in the nutrient solution, indicating fertilizer concentration. However, it doesn’t specify individual nutrient levels. Frequent testing of the nutrient solution is necessary, especially in closed systems where certain elements can accumulate.
pH Levels
The optimal pH range for hydroponic solutions is 5.8-6.3. Below 5.5, there is a risk of micronutrient toxicity and reduced availability of calcium and magnesium. Adjusting pH can be done using sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, or nitric acid.
Plant Nutrition
Hydroponics offers several advantages over traditional soil cultivation, including better control over nutrient availability. Plants require a balanced mix of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), along with trace elements.
Nutrient Formulations
Hydroponic nutrient formulations are designed for specific growth stages. It’s crucial to use nutrients formulated for hydroponics, as they differ from those intended for soil-based plants. For instance, nitrogen in hydroponic nutrients is provided in a water-soluble form (nitrate) rather than urea.
Nutrient Solution Temperature
Maintaining the nutrient solution temperature between 68-72°F (20-22°C) is ideal, mimicking natural soil conditions. Temperatures outside this range can lead to various plant issues.
Hydroponic Nutrient Solution Setup
- Water Quality: Monitor salinity and harmful elements like sodium, chloride, and boron.
- Nutrient Balance: Ensure all essential nutrients are present in the correct proportions.
By carefully managing these aspects, hydroponic growers can achieve optimal plant growth and health.
Summary for Instagram Reels and Infographics
Quick Tips for Growing Valerian and Managing Hydroponic Nutrients:
- Valerian: Easy to grow in temperate climates, thrives in humid areas, and has potent medicinal properties for anxiety and insomnia.
- Hydroponic Nutrients: Maintain proper pH (5.8-6.3), monitor EC for total dissolved salts, and ensure balanced nutrient formulations tailored for hydroponics.
These guidelines will help you cultivate valerian effectively and optimize your hydroponic systems for robust plant growth. Enjoy the benefits of these powerful plants and advanced growing techniques!
. DO IT YOURSELF! BUILD YOUR PERSONAL HYDROPONIC SETUP
Creating your own hydroponic system can be an exciting and rewarding project. To ensure success, it’s crucial to plan meticulously and avoid common pitfalls that can hinder your experiment. Here are step-by-step instructions and considerations to help you build an efficient and effective hydroponic setup.
Selecting the Right Vessels
The size and shape of your vessels can vary, but they must not leak water or react with the nutrient solution. Suitable materials include metals, plastic, ceramics, porcelain, and concrete. Ensure each vessel is covered with an insulating layer where it contacts the nutrient solution. Double-coating with bitumen paint works well, but avoid coal tar products which are toxic to plants. For larger setups, waterproof liners can be used in earthen ditches or wooden troughs, ensuring the film is phenol-free to prevent plant toxicity.
Choosing the Right Substrate
The substrate in which plants will grow must:
- Have large enough particles to prevent them from spilling out.
- Absorb and retain water to reduce the need for daily moisturizing.
- Resist decomposition and avoid rotting.
- Be chemically neutral to avoid affecting the nutrient solution.
Popular Substrate Options:
- Vermiculite: A mineral formed from hydrothermal changes in mica, vermiculite expands when heated and has a light, stable structure. It is chemically inert, absorbs water well, and retains its structure, making it ideal for hydroponics.
- Pumice and Foamy Lava: These sponge-like volcanic rocks are highly absorbent but may contain free lime, which can react undesirably with the nutrient solution. Washing with diluted sulfuric acid and thorough rinsing can neutralize these components.
- Blast Furnace Slag: This gravel-like byproduct of iron smelting is highly porous but contains high alkalinity. Similar to pumice, it requires chemical treatment with sulfuric acid to remove lime before use.
- Coal Slag: Well-calcined coal or coke slag is a low-cost alternative, but ensure it’s free from toxic sulfur compounds through acid treatment.
- Quartz Sand, Basalt Chips, Crushed Granite: These are chemically neutral but non-absorbent. They can be mixed with other substrates to improve water absorption.
- Peat Mixtures: Adding peat to gravel or using pure peat can enhance aeration and nutrient absorption due to humic substances in peat that aid plant growth.
Preparing Substrates
To ensure substrates are safe and effective:
- Wash pumice and slag with diluted sulfuric acid to neutralize lime and other reactive compounds.
- Rinse thoroughly with water until a slightly acidic reaction is detected on litmus paper.
- For slag, add 10% silica sand to improve structure and ease of handling.
- Mix peat with gravel to improve aeration and nutrient absorption.
Humic Substances
Recent studies show that humic substances in substrates can:
- Increase nutrient solubility, enhancing plant nutrient absorption.
- Provide a buffering effect to maintain a stable nutrient solution.
- Contain growth substances that promote plant development.
Mixing peat with inorganic substrates can provide these benefits, especially for plant species that thrive with humic substances.
Setting Up Your Hydroponic System
- Construct Vessels: Choose appropriate materials and ensure they are coated or lined as needed.
- Prepare Substrate: Select and prepare your substrate according to the guidelines above.
- Planting: Ensure plants are securely placed in the substrate and roots are well covered.
- Nutrient Solution: Prepare and regularly check the nutrient solution for pH and nutrient levels.
By following these guidelines, you can build a functional hydroponic system tailored to your needs, ensuring your plants thrive without the use of traditional soil. Happy growing!
About Us
Welcome to Agriculture Novel, your go-to source for in-depth information and insights into the world of agriculture, hydroponics, and sustainable farming. Our mission is to educate, inspire, and empower a new generation of farmers, hobbyists, and eco-conscious enthusiasts. Whether you’re interested in traditional farming practices or modern innovations, we aim to provide comprehensive guides, expert tips, and the latest updates in agriculture and urban farming.
At Agriculture Novel, we believe in the power of knowledge to transform the way we grow, sustain, and nourish our world. Explore our articles on topics like Fruit Growing Guide, Hydroponics, Plant Deficiency Guide, and more.
Thank you for joining us on this journey towards a greener, more sustainable future!
About Agronique Horizon
At Agronique Horizon, we specialize in delivering comprehensive digital marketing and web development solutions tailored for the agriculture and hydroponics industries. From custom website design and app development to social media management, we provide end-to-end support for brands aiming to make a meaningful impact. Our team also offers innovative solutions for the real estate sector, bringing precision and visibility to your projects. Learn more about our services here and discover how we can elevate your digital presence
👥 Readers added context they thought people might want to know
Agri-X VerifiedCurrent formatting suggests planting in June. However, 2025 IMD data confirms delayed monsoon. Correct action: Wait until July 15th for this specific variety.
Contribute to the truth. Log in to verify.



